ECON 366: Energy Economics
Topic 2.2: Oil and Gas Extraction
Andrew Leach, Professor of Economics and Law
Oil and gas topology
Oil and gas topology
Oil and gas topology
Oil and gas topology
Shale or Tight Oil and Gas
- oil and gas trapped in low-permeability deposits
- unlike conventional resources, shale or tight oil and gas requires active efforts other than drilling to release the hydrocarbons
- Resources include previously-drilled areas where new extraction techniques have opened up new layers or made known resources more productive
Oil and gas topology
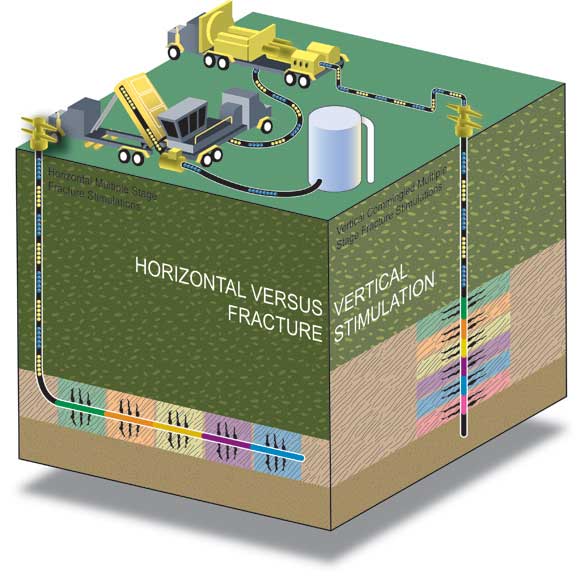
Shale or Tight Oil and Gas: Fracking and Proppant
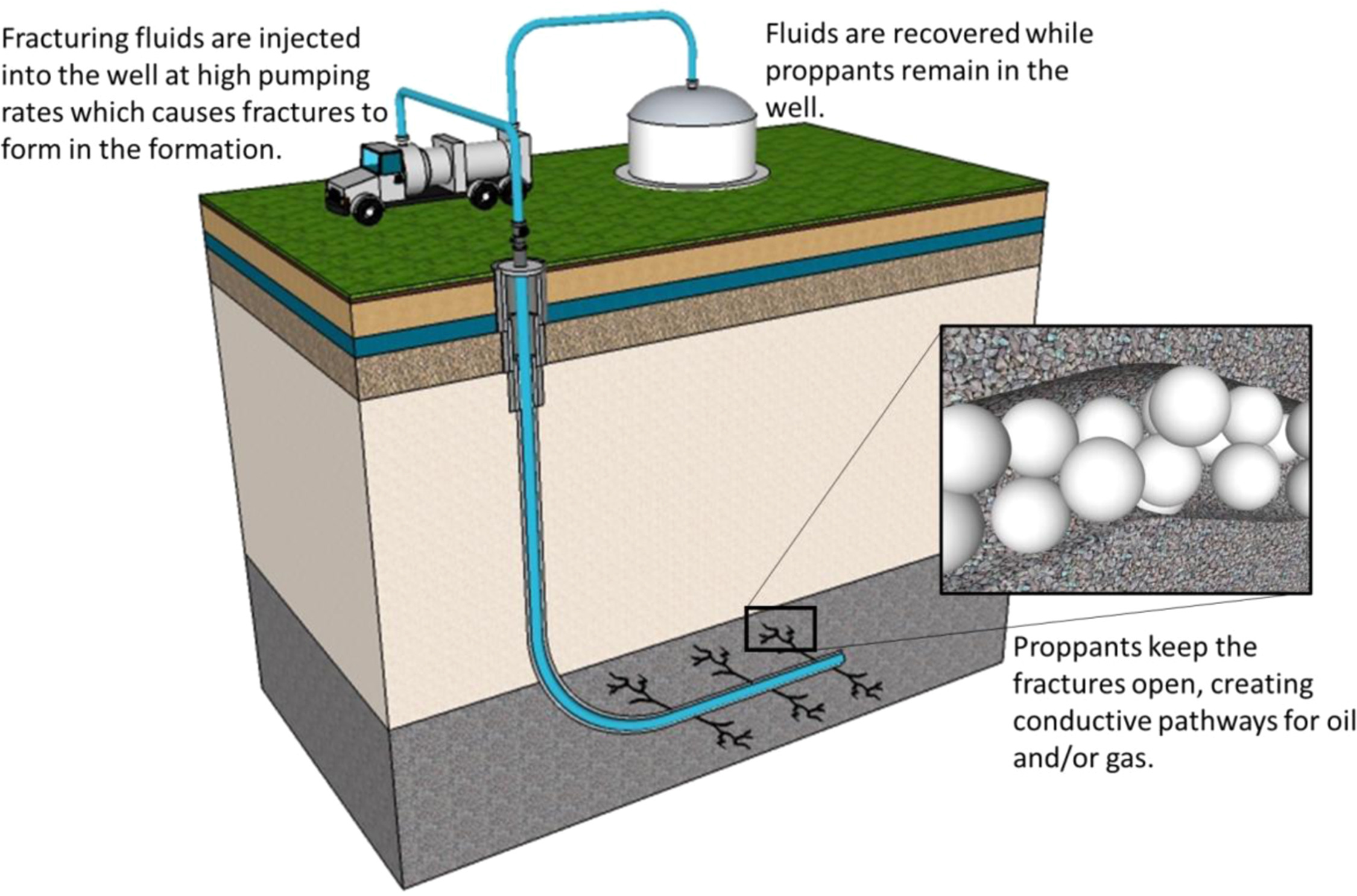
Katrina D. Pangilinan, Al Christopher C. de Leon, Rigoberto C. Advincula, Polymers for proppants used in hydraulic fracturing, Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, Volume 145, 2016, Pages 154-160, ISSN 0920-4105, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2016.03.022
Oil and gas topology
Oil and gas plays

Oil and gas plays

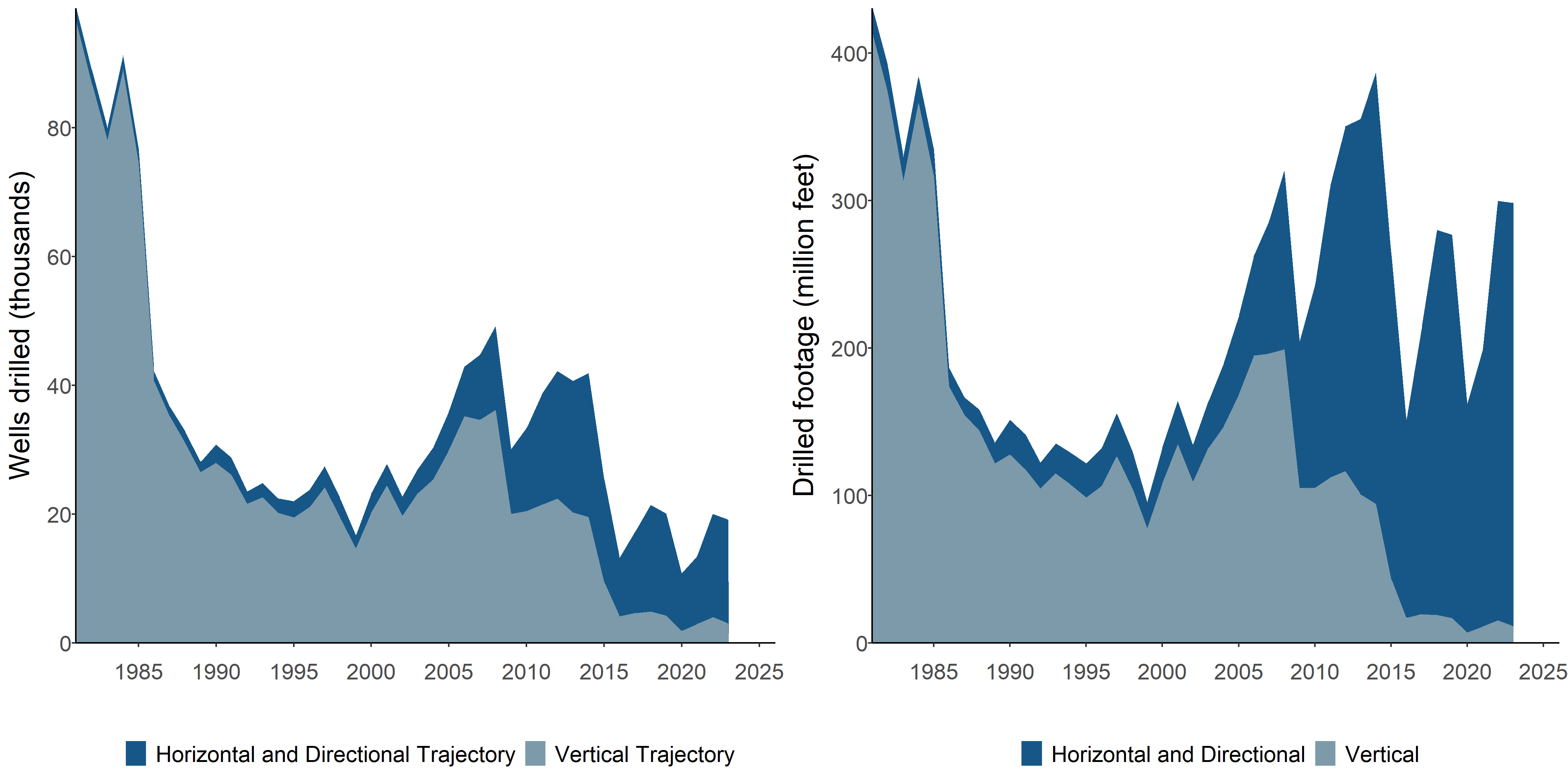
The Speed of the Shale Gas Revolution

US Oil Production
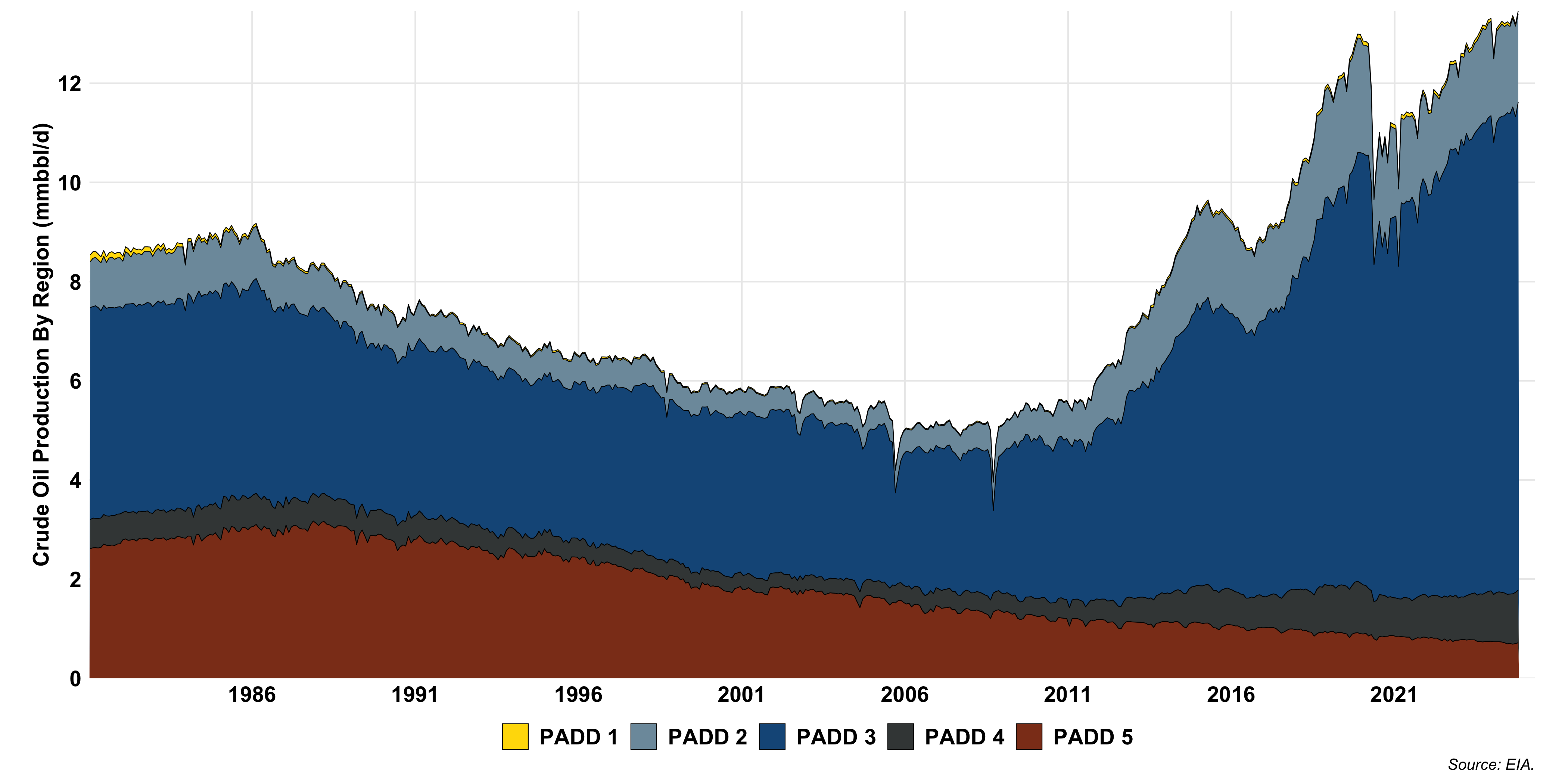
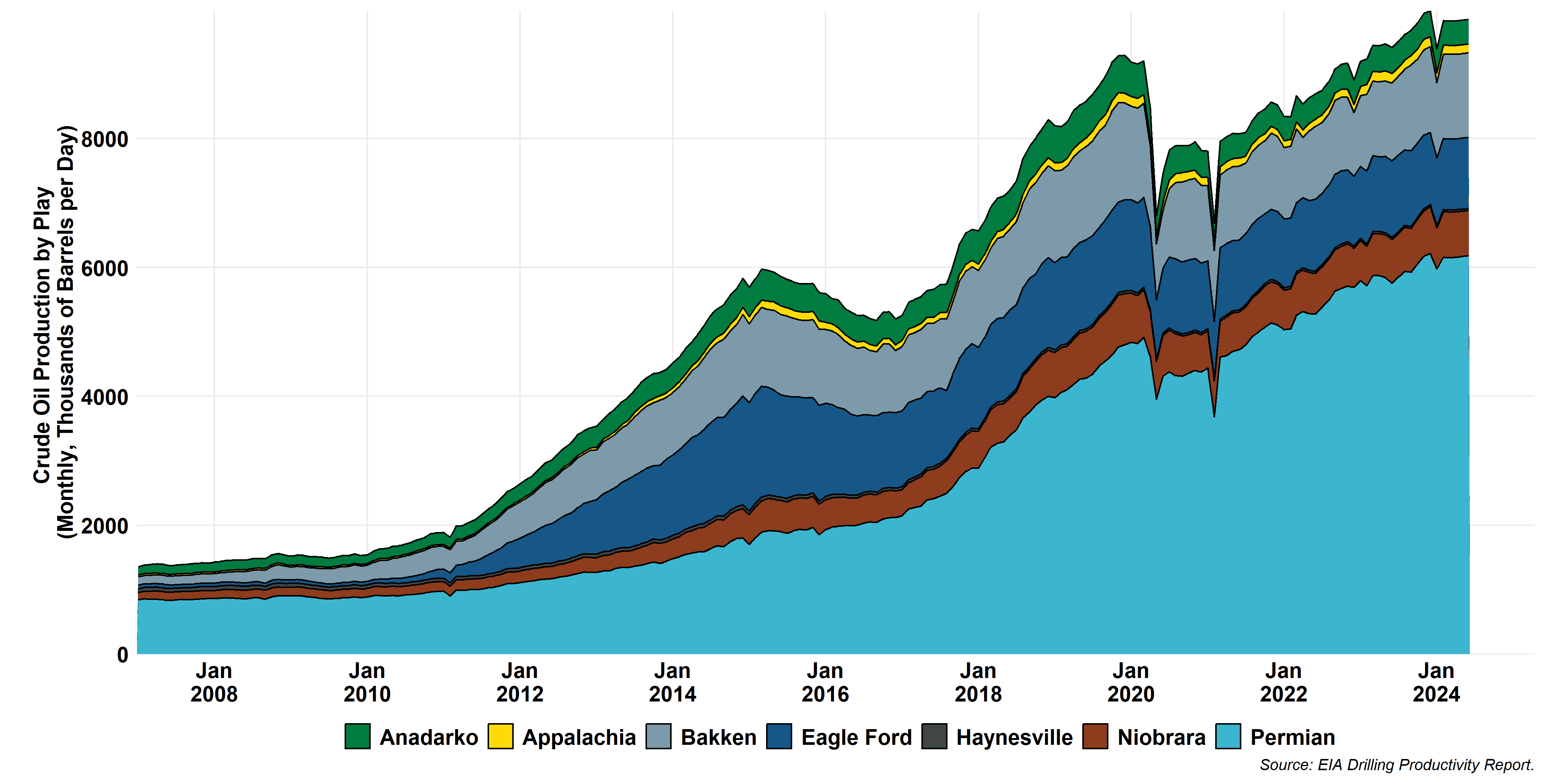
LTO Production by Play
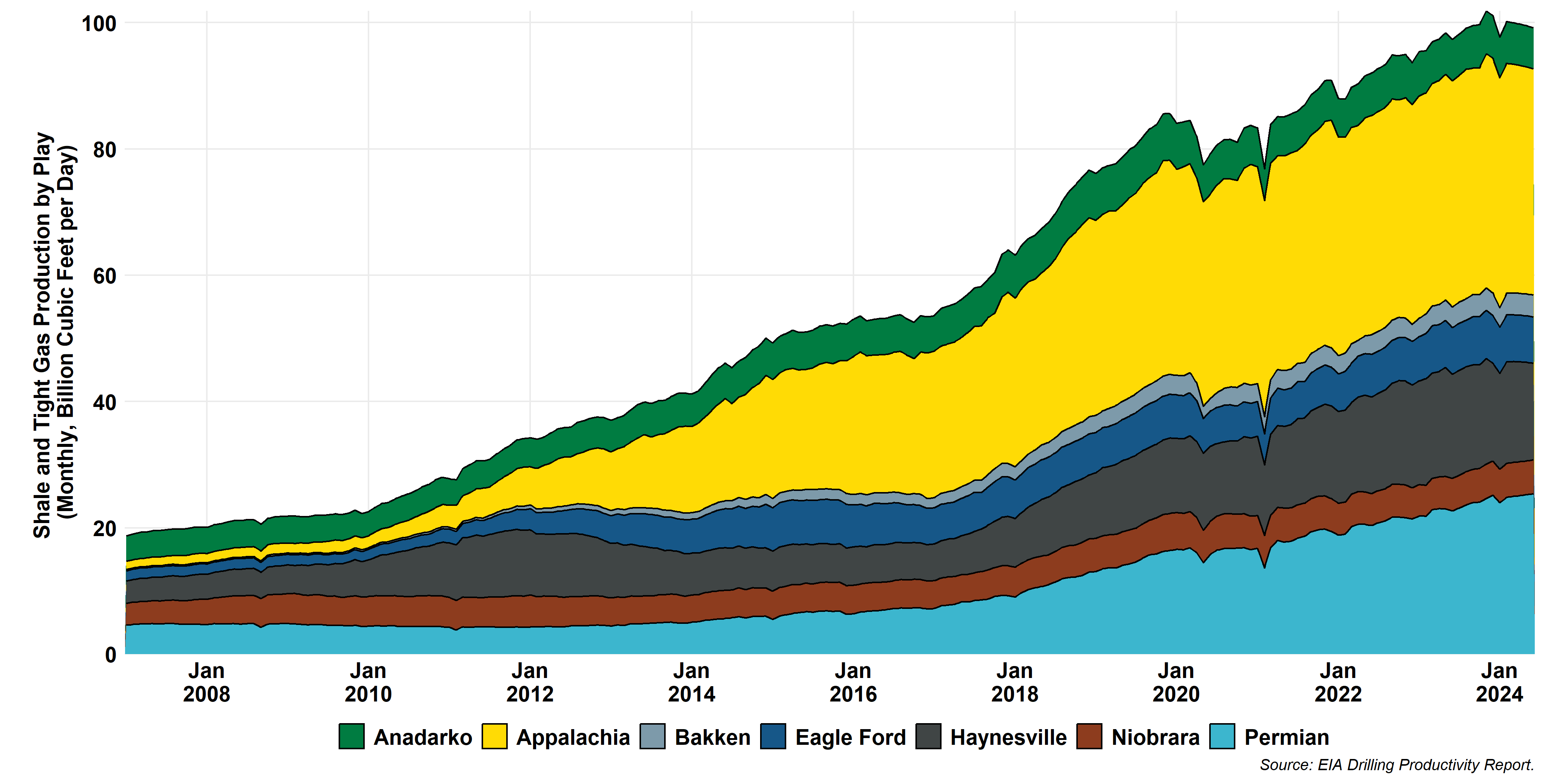
Tight/Shale Gas Production by Play
Oil and gas plays

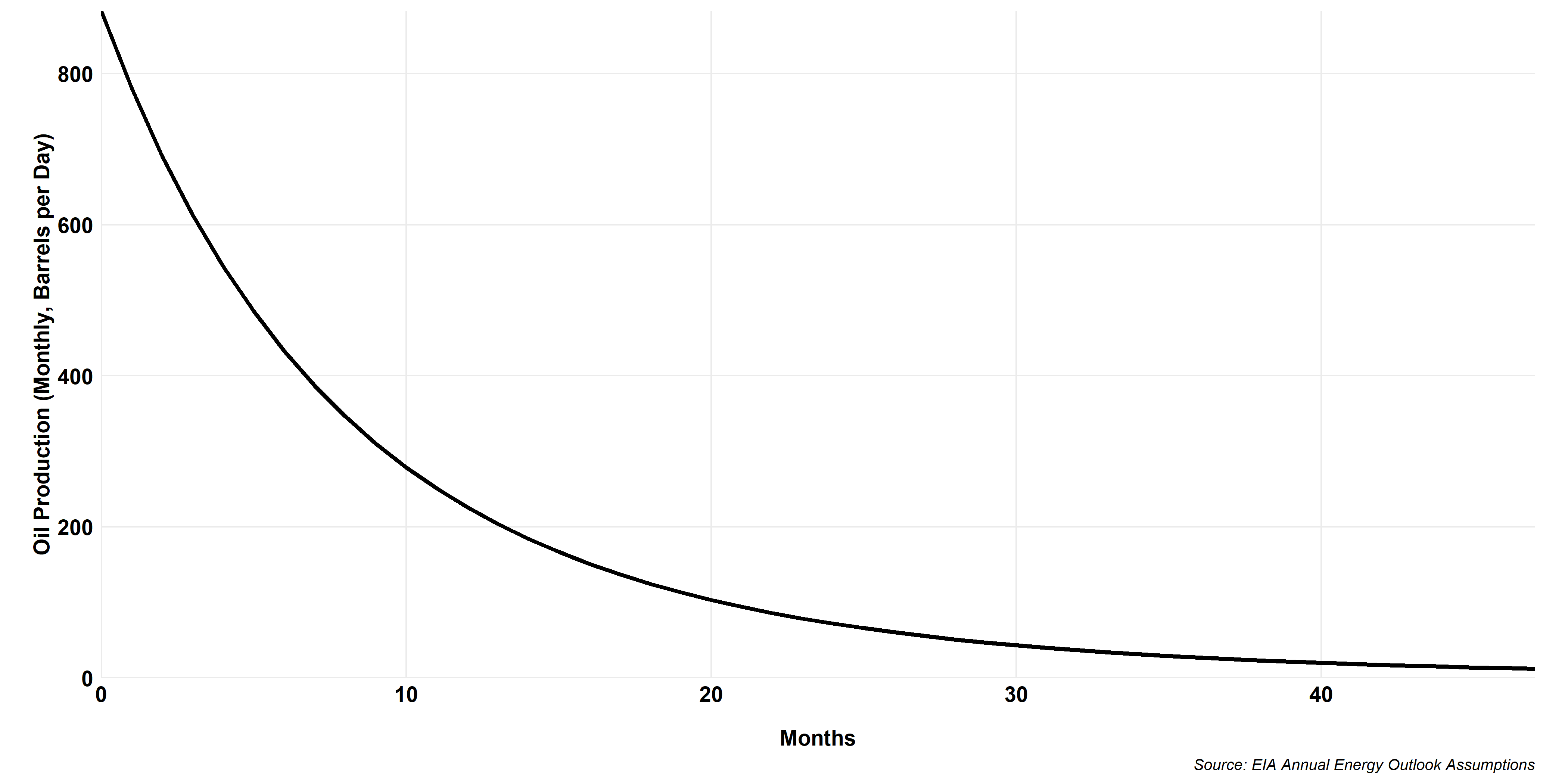
Bakken Oil Type Curve
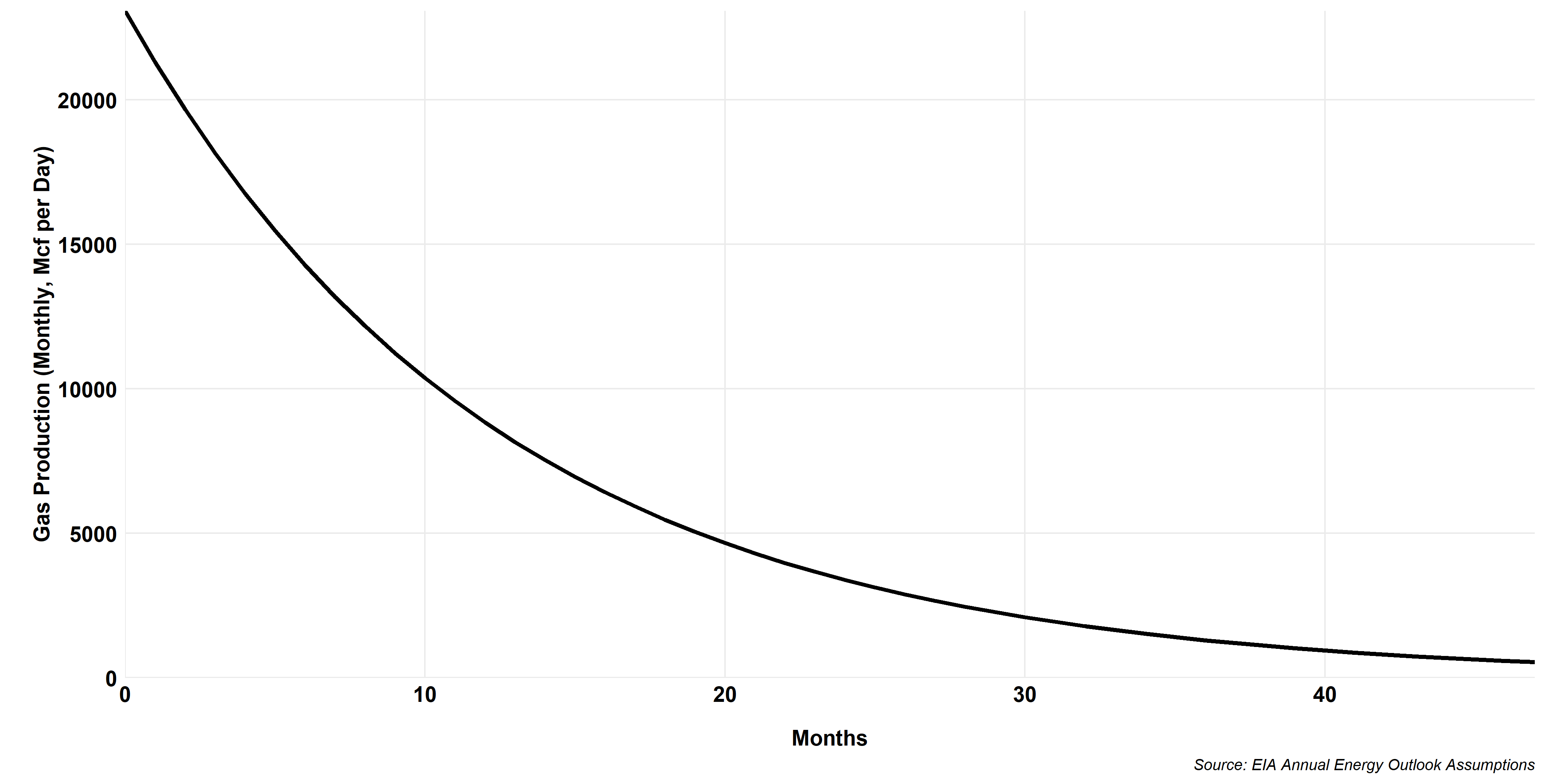
Haynesville Shale Gas Type Curve
Evolving production dynamics
Tight Oil and Shale Gas New Well Productivity by Play
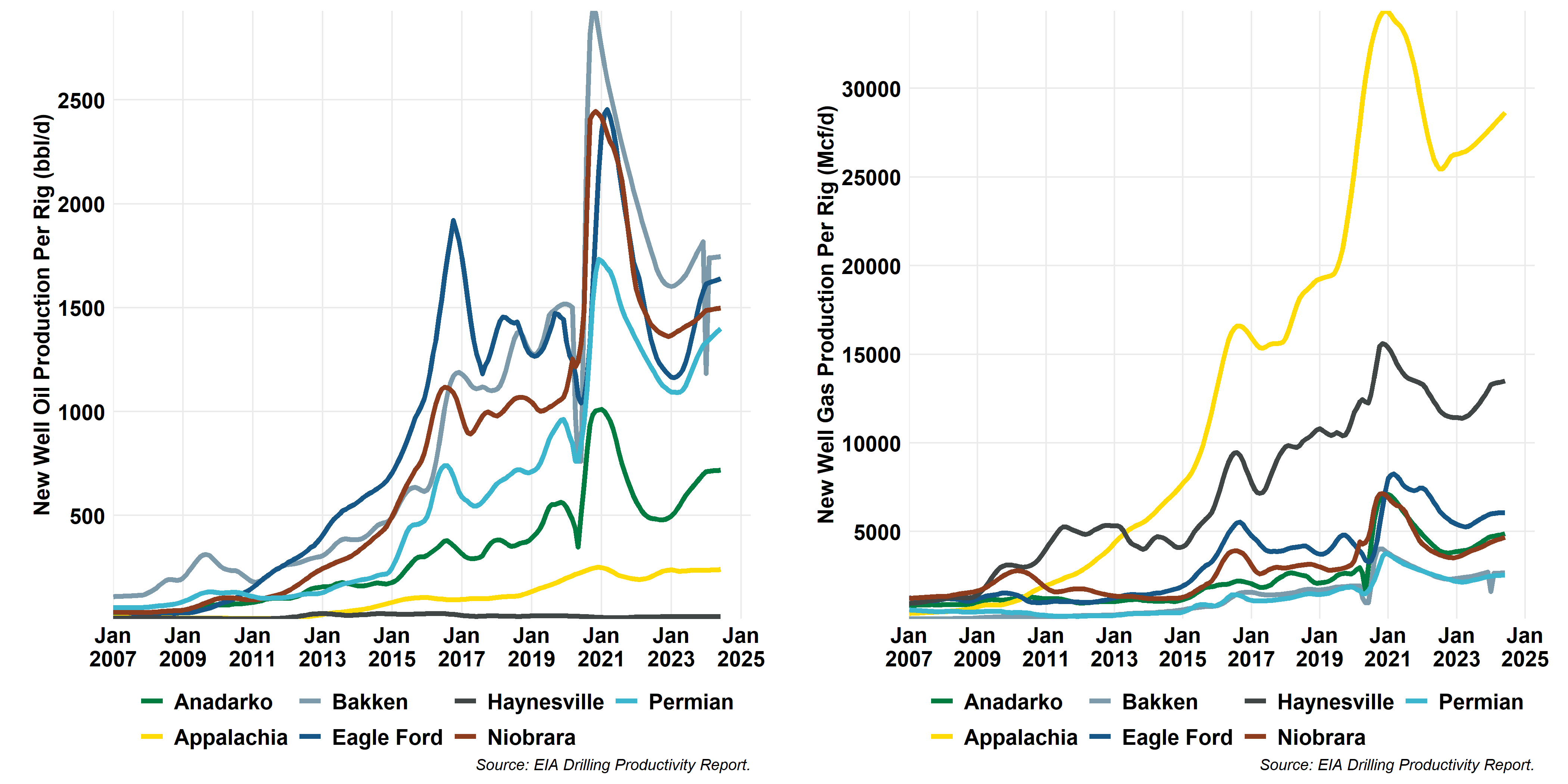
Evolving production dynamics
Evolving production dynamics
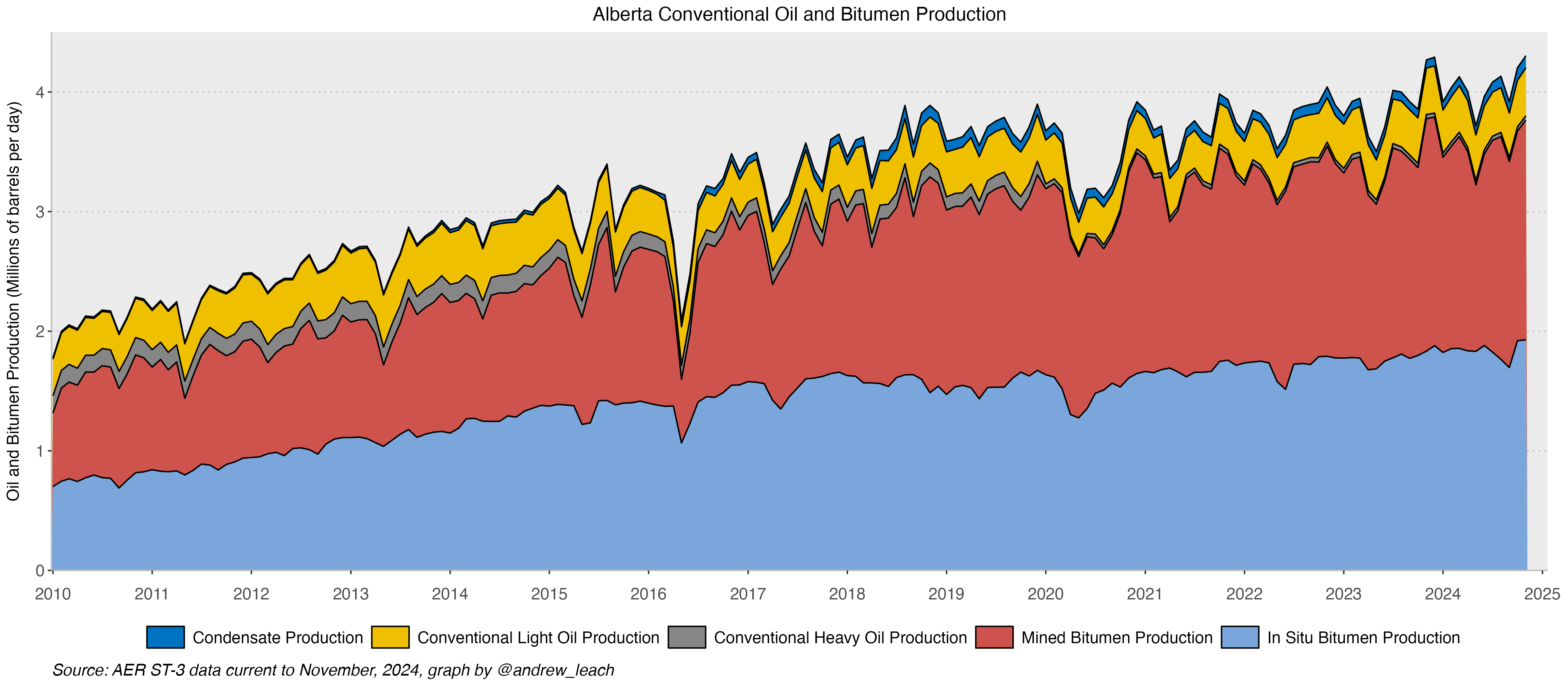
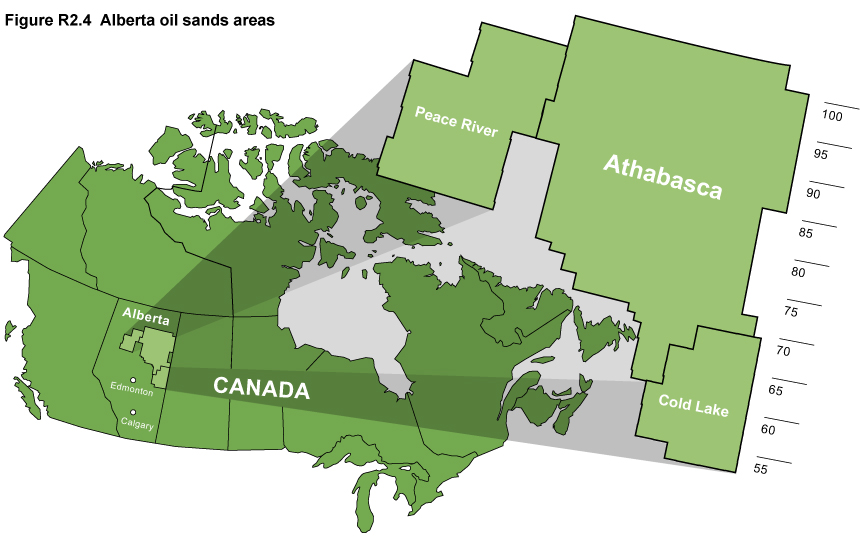
Canadian Oil Sands
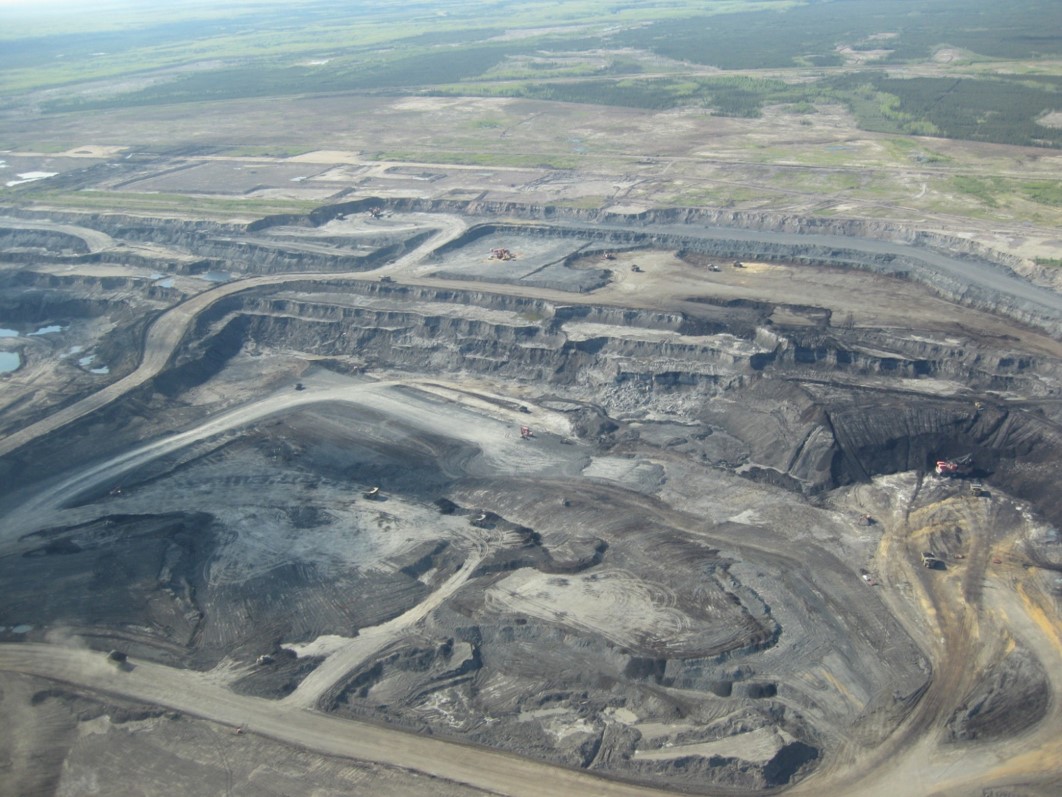

Canadian Oil Sands Leased Area
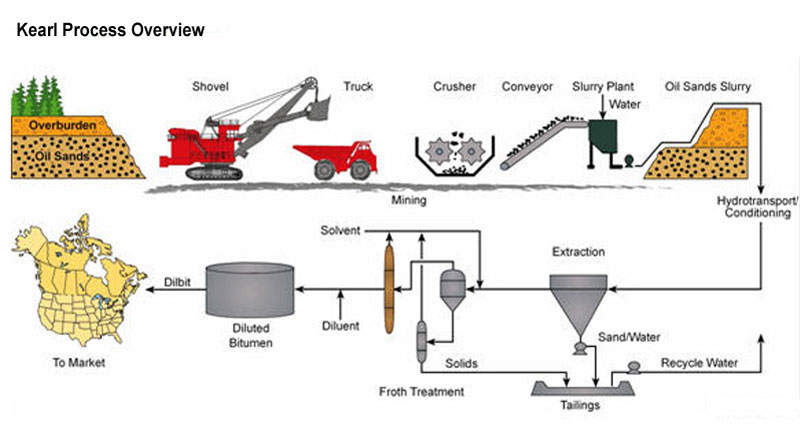
Oil sands Mining

Oil sands mine
- Trucks and shovels extract oil sands ore
- Bitumen is separated from the sand and clay mixture using hot water and naphtha and/or paraffins
- Bitumen is either diluted and shipped or upgraded to synthetic crude oil (SCO)
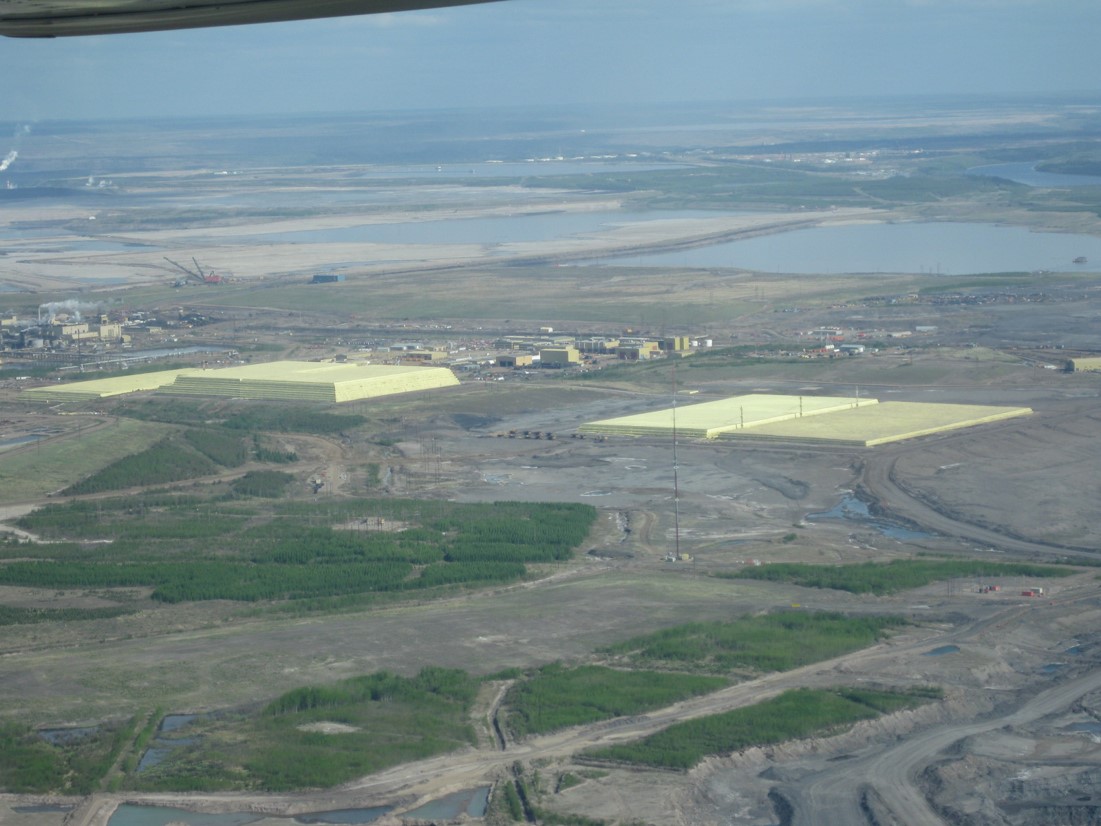
- By-products are petroleum coke, sulphur, tailings
Suncor oil sands plant
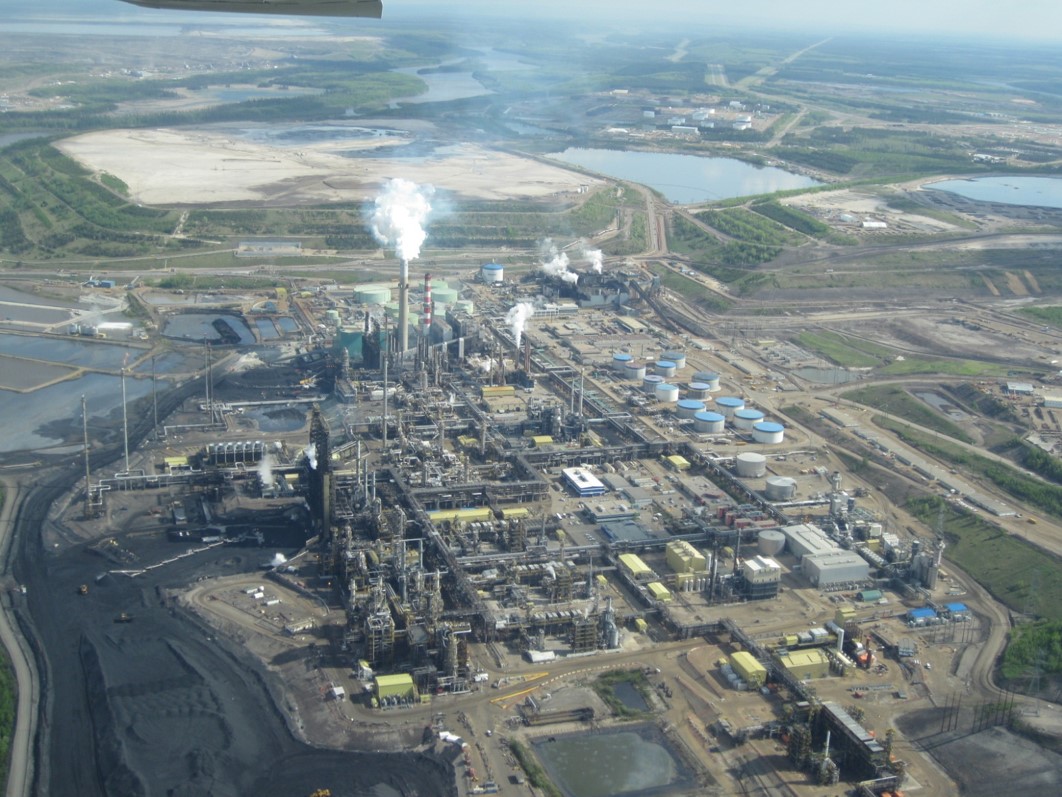

Syncrude oil sands plant
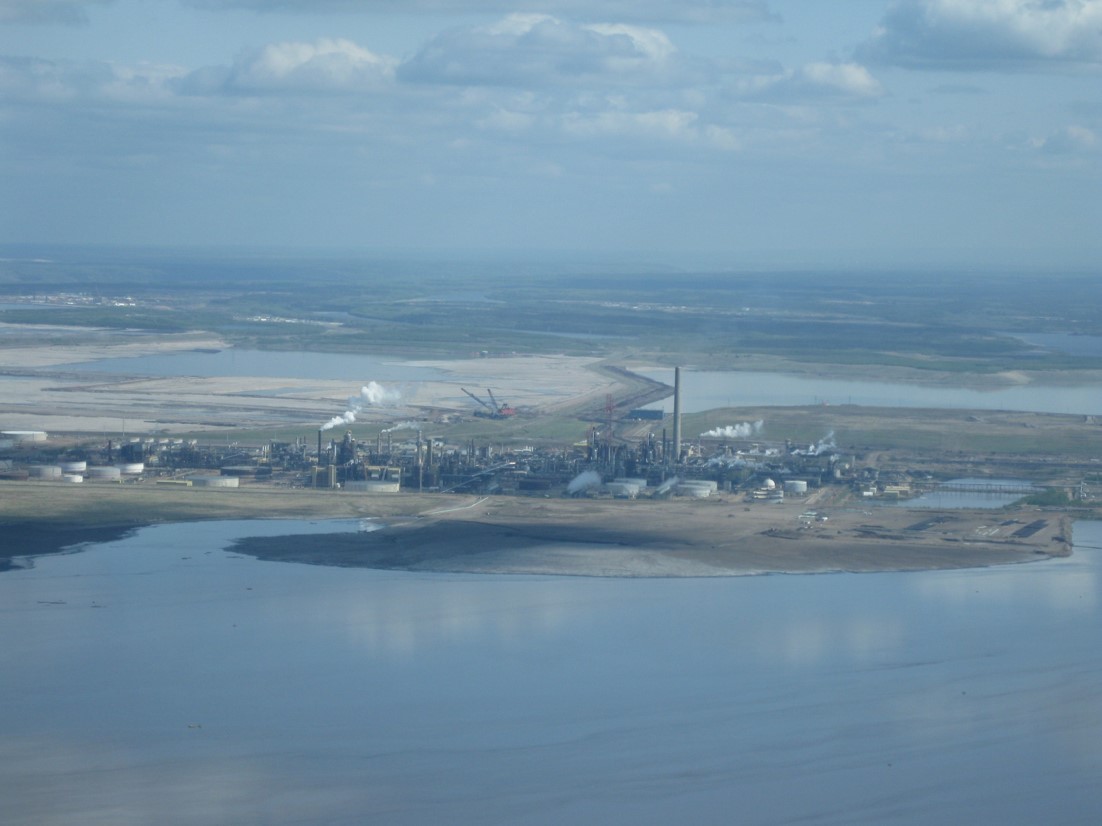

Syncrude sulphur piles

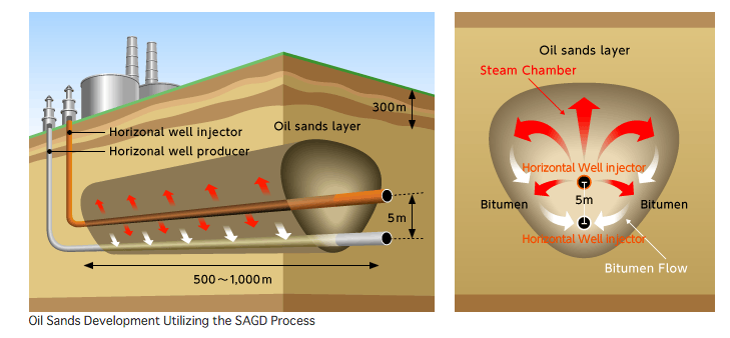
Steam-Assisted Gravity Drainage (SAGD)
SAGD is a process that uses steam to heat the reservoir to reduce the viscosity of the bitumen. This requires at least two horizontal wells to be drilled: an injector on top and an underlying producer, generally located 5 m below the injector. The upper well injects steam into the reservoir, creating a steam chamber and heating the bitumen up to 230oC, reducing its viscosity and allowing it to flow.
With the help of gravity, the now-mobile bitumen and condensed steam flow to the lower producer well where they are pumped to the surface for transport, separation, and partial upgrading.
Water and/or gas reservoirs, which are in association with the bitumen reservoirs, may act as thief zones, stealing steam energy.
See AER ST-98
Oil sands in situ
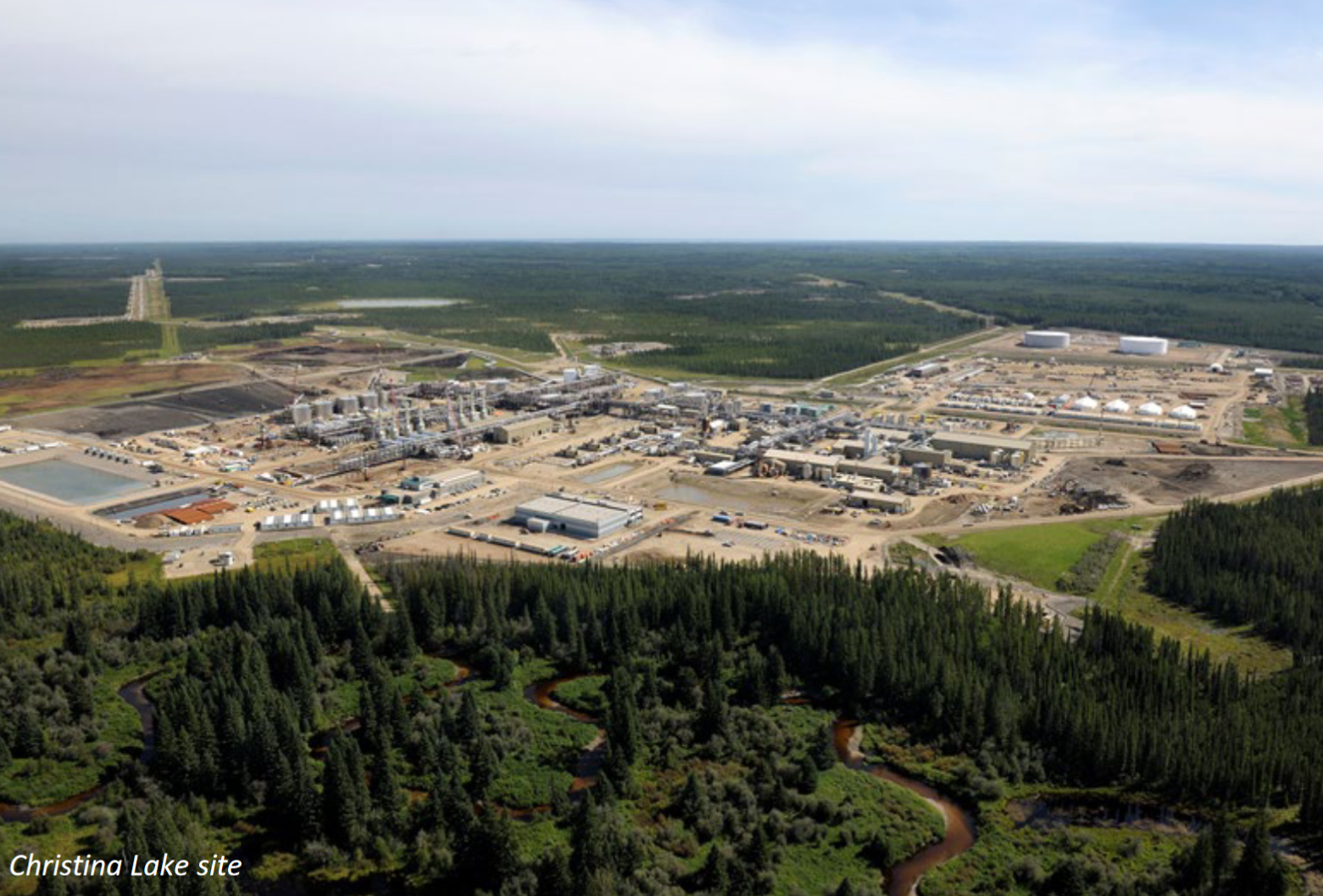

Oil sands in situ
- Natural gas or other fuel used to create steam which heats oil underground and renders it less viscous
- Oil flows out through production wells
- Two main types: Steam-assisted gravity drainage (SAGD)
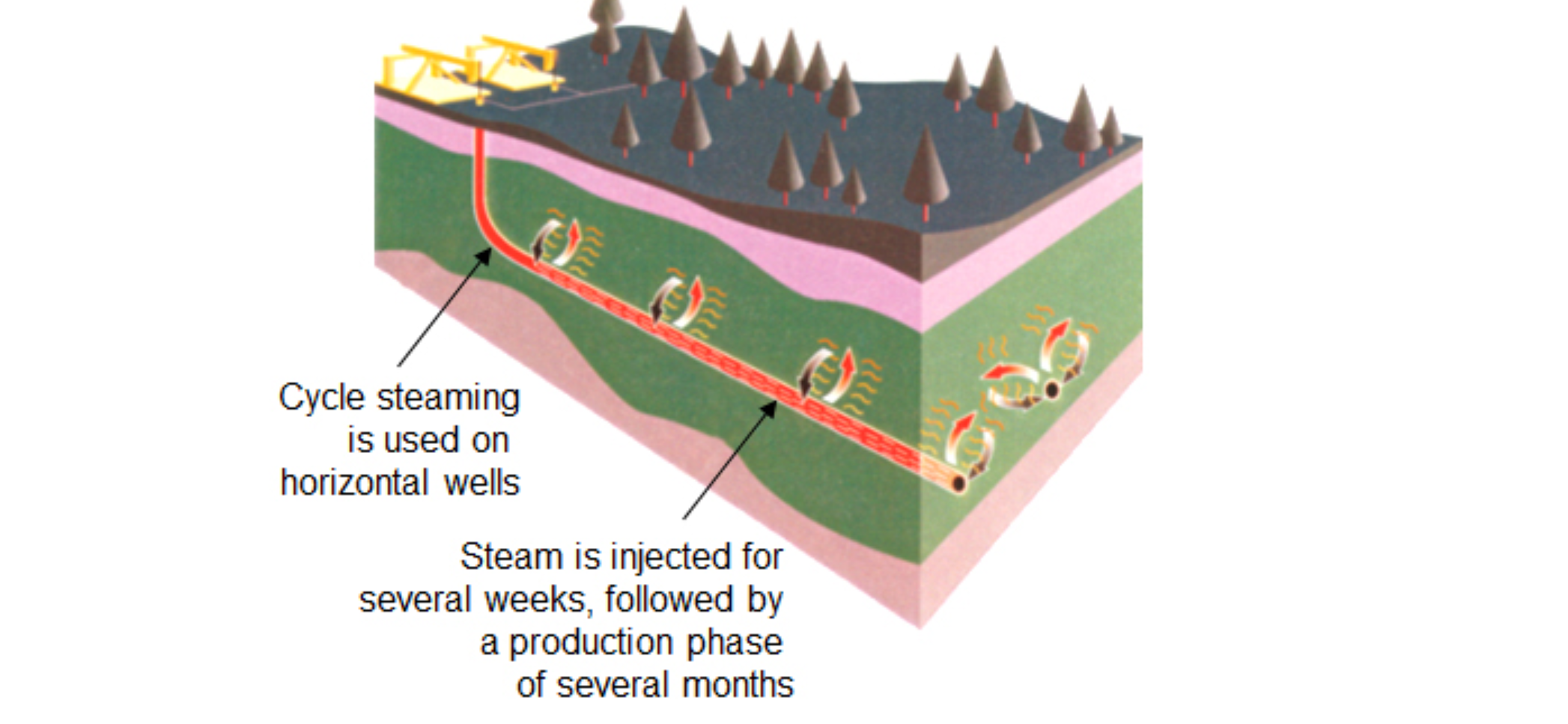
Cyclic-Steam Stimulation (CSS)
Cyclic-steam stimulation (CSS) also known as the "huff and puff" method, consist of 3 stages: injection, soak, and oil production. Steam is injected into a well at a temperature of 300 to 340°C for a period of weeks to months to heat the oil in the surrounding reservoir to recover approximately 20% of the original bitumen in-place (OBIP). In comparison steam-assisted gravity drainage recovers over 50% of OBIP.
This process is predominantly a vertical-well process, but it could be applied on multilateral horizontal legs and would consist of alternately injecting steam and producing heavy oil and steam condensate. CSS works best in thick pay zones(>10m) with high porosity sands (30%).
See AER ST-98
Oil sands in situ
- Natural gas or other fuel used to create steam which heats oil underground and renders it less viscous
- Oil flows out through production wells
- Two main types: cyclic-steam-stimulation (CSS)
Oil sands in situ
- Key metric for in-situ oil sands is the steam:oil ratio (SOR)
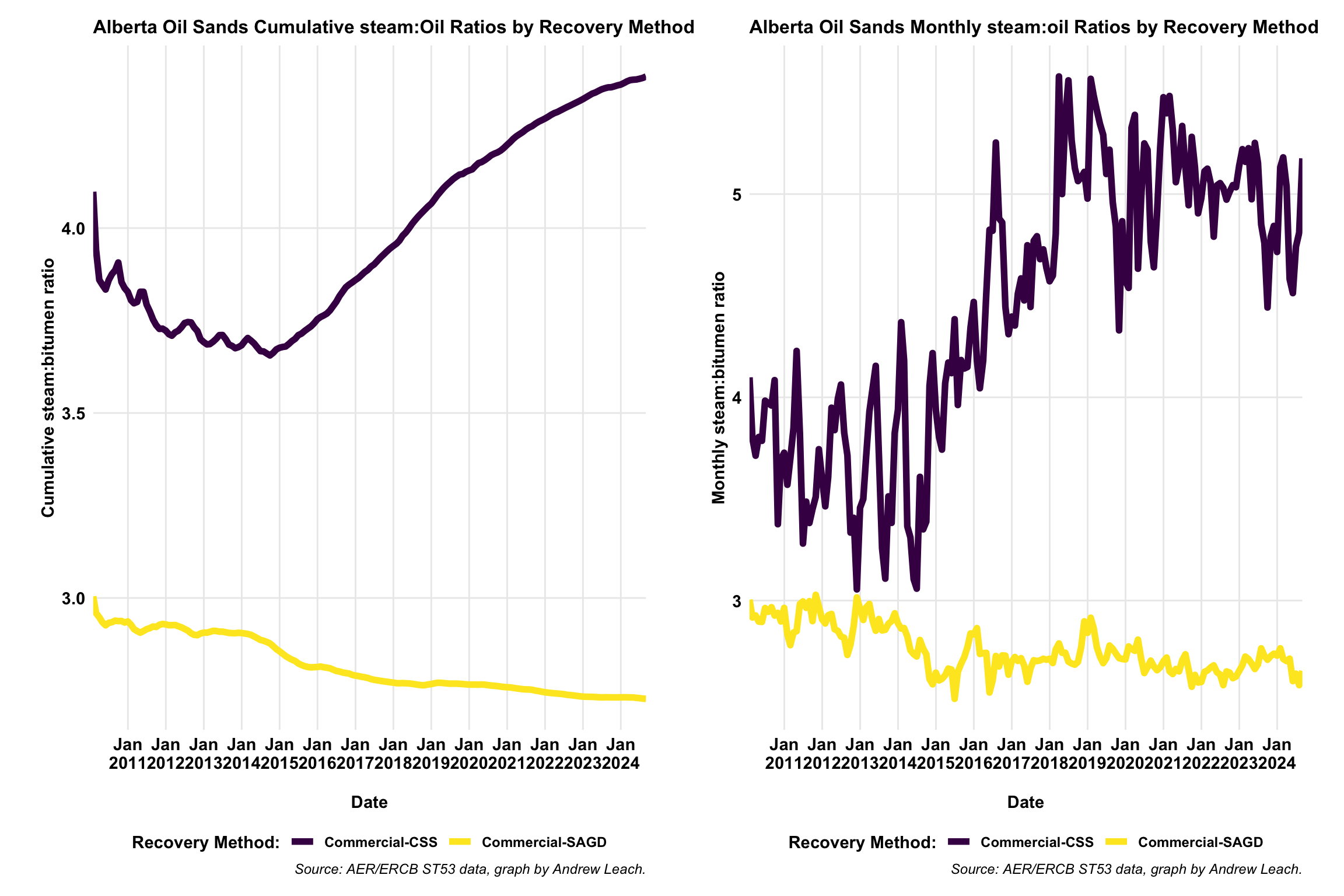
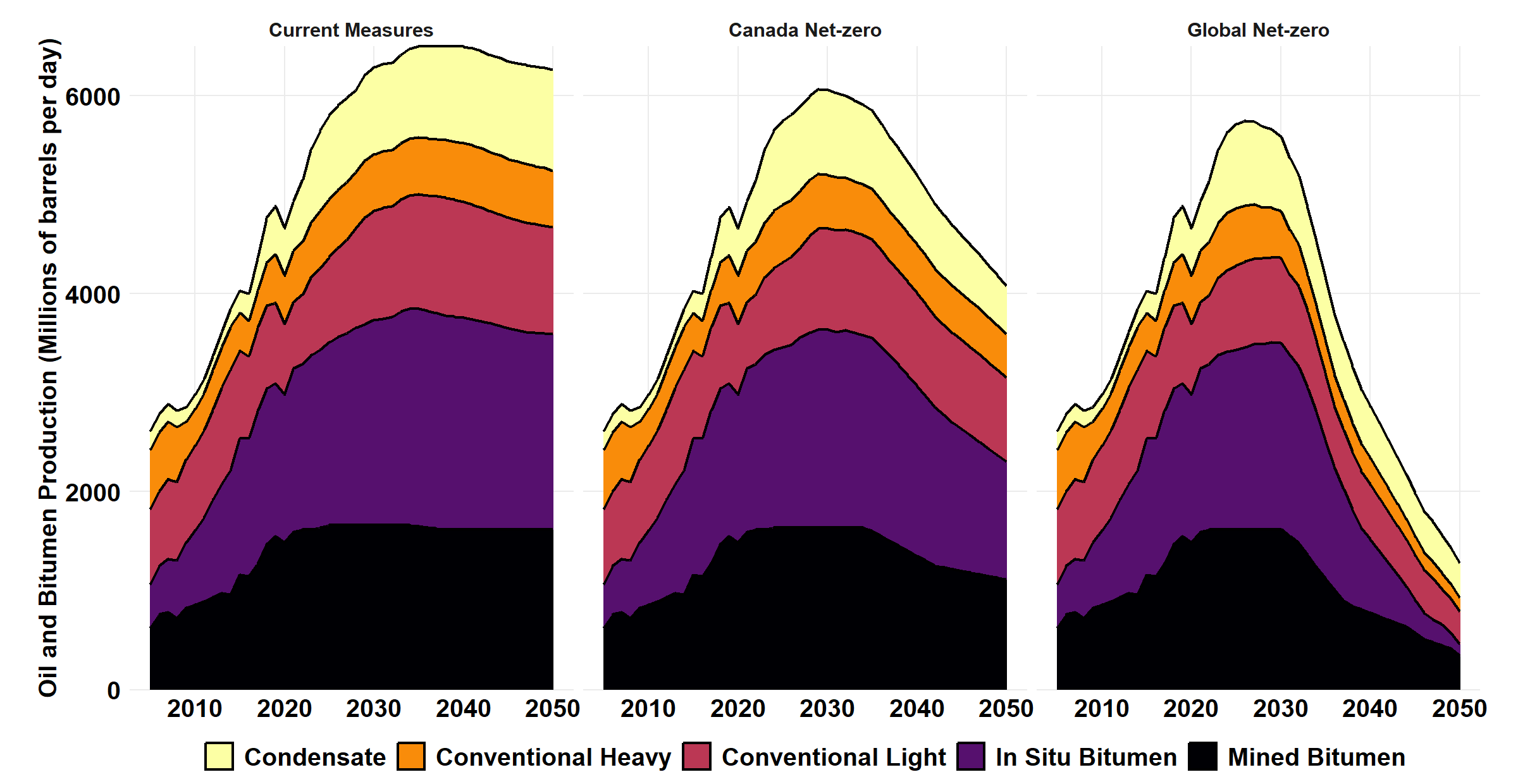
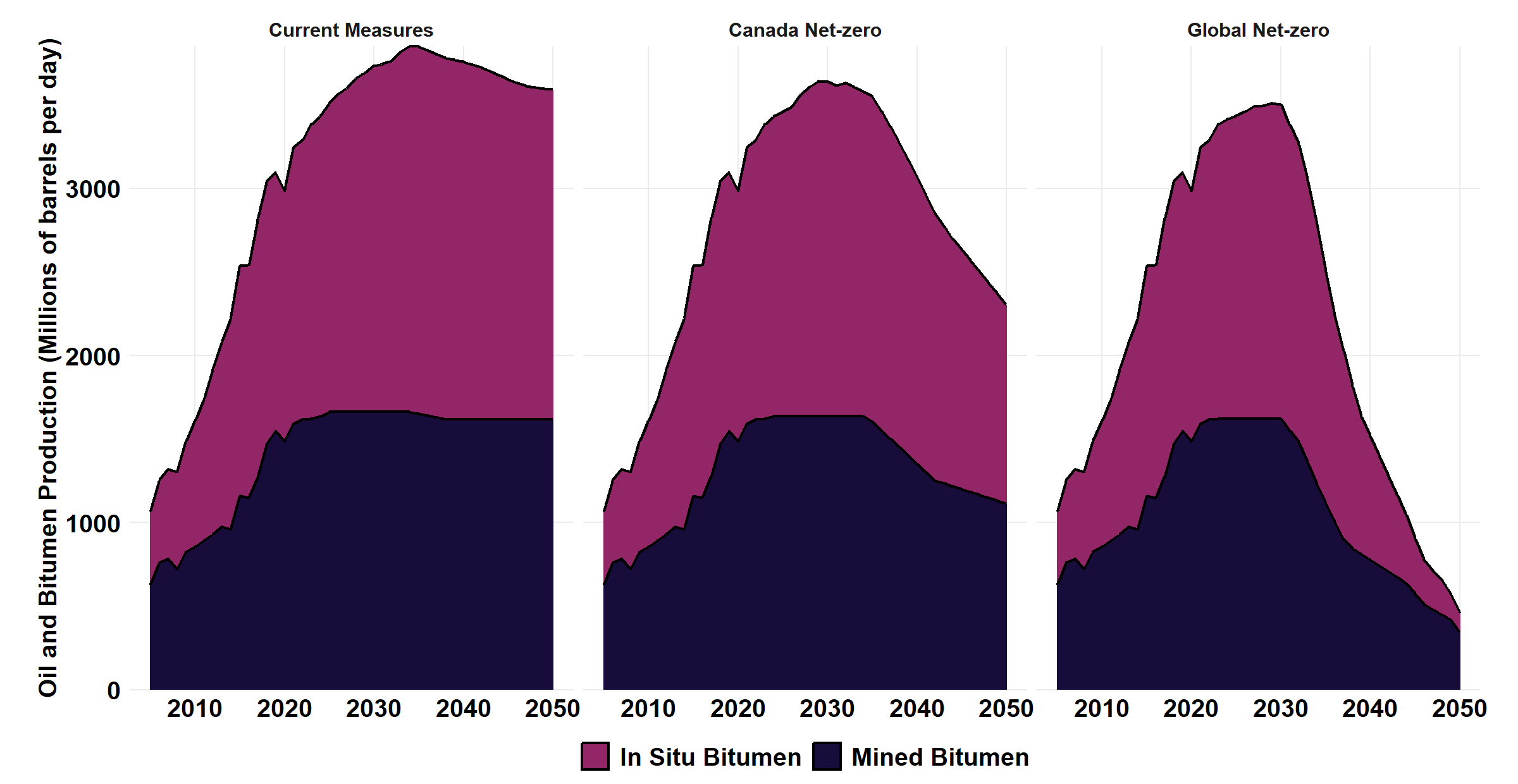
Canadian Oil Sands Production